An pulmonary embolism is a blockage in the pulmonary artery, which supplies the blood to the lungs. It is one of the most widely recognized cardiovascular diseases. The blockage, normally a blood clot, keeps oxygen from arriving at the tissues of the lungs. This implies it can be life-threatening. Here are treatment for pulmonary embolism, causes and symptoms.
“Embolism” originates from the Greek émbolos, signifying “plug” or “attachment.”
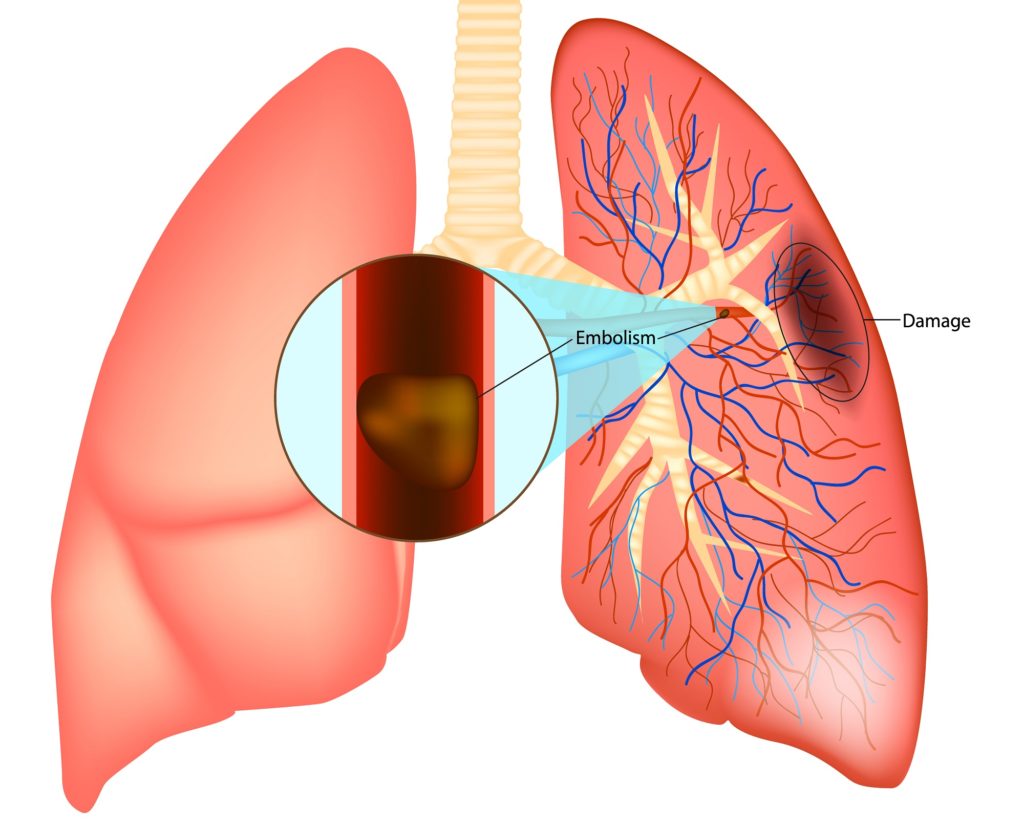
In an pulmonary embolism, the embolus, forms in a single piece of the body, it courses all through the blood supply, and afterward it hinders the blood moving through a vessel in another piece of the body, to be specific the lungs.
An embolus is not the same as a blood clot, which structures and remains in one spot.
Symptoms
Here are some symptoms of pulmonary embolism include :
- difficulty catching breath, which may develop either suddenly or over time
- chest pain, a sharp, stabbing pain that might become worse when breathing in
- a cough, normally dry but possibly with blood, or blood and mucus
- rapid breathing
- increased or irregular heartbeat
- dizziness
Causes
Here are some pulmonary embolism causes include :
An pulmonary embolism happens when an embolus, normally a blood clot, blocks the blood moving through a vein that takes care of the lungs.
A blood clot may begin in an arm or leg, known as deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
From that point onward, it breaks free and goes through the circulatory system towards the lungs. There, it is too enormous to even consider passing through the little vessels, so it forms a blockage.
This blockage prevents blood from streaming into a piece of the lung. This makes the influenced area of the lung bite the dust through absence of oxygen.
Once in a while, an pulmonary embolism can result from an embolus that is shaped from fat beads, amniotic liquid, or some other molecule that enters the bloodstream.
Also Read : How To Lower Your Blood Pressure Safely ?
Treatment
Here are some Treatment for pulmonary embolism include :
- prevent new clots from forming
- stop the clot from growing
- destroy or remove any existing clot
An initial phase in treating most embolisms is to treat stun and give oxygen treatment.
Anticoagulant prescriptions, for example, heparin, enoxaparin, or warfarin are generally given to help thin the blood and prevent further clotting.
People who need anticoagulant medications should look for treatment with an anticoagulant management service, not their essential consideration doctor.
Clot-busting drugs drugs called thrombolytics may likewise be controlled. Nonetheless, yet these convey a high danger of excessive bleeding. Thrombolytics include Activase, Retavase, and Eminase.
On the off chance that the patient has blood pressure, dopamine might be given to build pressure.
The patient will ordinarily need to take meds normally for an inconclusive measure of time, as a rule in any event 3 months.